Server Startup: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
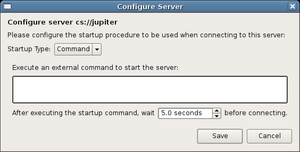
If the user attempts to connect to a server without any configuration, creates a new server, or selects ''Edit Server'' in the "Manage Servers" dialog, the "Configure Server" dialog opens. | If the user attempts to connect to a server without any configuration, creates a new server, or selects ''Edit Server'' in the "Manage Servers" dialog, the "Configure Server" dialog opens. | ||
=== Command Startup === | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
For new server configurations, the dialog defaults to a ''Command'' startup configuration. In this case ParaView will run an external command to start the server. The external command will be run using exec() (Posix systems) or CreateProcess() (Win32), so shell-specific functionality such as redirection or "&" cannot be used. | For new server configurations, the dialog defaults to a ''Command'' startup configuration. In this case ParaView will run an external command to start the server. The external command will be run using exec() (Posix systems) or CreateProcess() (Win32), so shell-specific functionality such as redirection or "&" cannot be used (unless you invoke a specific shell directly). | ||
The following environment variables are used to communicate connection parameters to the command: | |||
* PV_CONNECTION_URI | |||
* PV_CONNECTION_SCHEME | |||
* PV_SERVER_HOST | |||
* PV_SERVER_PORT | |||
* PV_DATA_SERVER_HOST | |||
* PV_DATA_SERVER_PORT | |||
* PV_RENDER_SERVER_HOST | |||
* PV_RENDER_SERVER_PORT | |||
* PV_USERNAME | |||
Sample command to start a server on the local host (Win32): | |||
cmd /c start /b pvserver --server-port=%PV_SERVER_PORT% --use-offscreen-rendering | |||
Sample command to start a server on the local host (GNU/Linux): | |||
python -c "import os; os.system('pvserver --use-offscreen-rendering &')" | |||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 66: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | |||
=== Manual Startup === | |||
<table> | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 5 August 2006
Overview
Past versions of ParaView have required users to start client and server manually, specifying connection protocols and parameters at the command-line. ParaView3 improves the user experience by allowing users to start the client and make/break server connections using the client's graphical user interface.
For this functionality to work, ParaView must be properly configured to start remote servers. Startup procedures are expected to vary from site-to-site, due to differences in network topology, firewalls, address translation, logging requirements, etc. To accomodate this, a flexible mechanism allows users to run arbitrary commands on a per-server and/or per-connection-scheme basis at server startup.
Managing Servers
|
The collection of configured servers can be accessed through the "Manage Servers" dialog, which presents a listing of all servers that are already configured for automatic startup. The dialog contains standard controls for editing, deleting, and adding new server configurations. |
Configuring New Servers
|
If the user chooses Add Server in the "Manage Servers" dialog, the "Configure New Server" dialog opens. The user is prompted to select the type of server connection to configure (see Server Resources), and the host or hosts that will be used by the new configuration. |
Editing Server Configuration
If the user attempts to connect to a server without any configuration, creates a new server, or selects Edit Server in the "Manage Servers" dialog, the "Configure Server" dialog opens.
Command Startup
|
For new server configurations, the dialog defaults to a Command startup configuration. In this case ParaView will run an external command to start the server. The external command will be run using exec() (Posix systems) or CreateProcess() (Win32), so shell-specific functionality such as redirection or "&" cannot be used (unless you invoke a specific shell directly). The following environment variables are used to communicate connection parameters to the command:
Sample command to start a server on the local host (Win32): cmd /c start /b pvserver --server-port=%PV_SERVER_PORT% --use-offscreen-rendering Sample command to start a server on the local host (GNU/Linux): python -c "import os; os.system('pvserver --use-offscreen-rendering &')"
|
Manual Startup
|
Users who prefer to start servers manually can specify as such in the "Configure Server" dialog. In this case, the user must ensure that the server(s) are running before attempting to connect with the ParaView client. |