ParaQ:Scripting: Difference between revisions
(→Design) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* SM is designed to provide such an interface | * SM is designed to provide such an interface | ||
* SM is already wrapped into Tcl, Python and client/server streams | * SM is already wrapped into Tcl, Python and client/server streams | ||
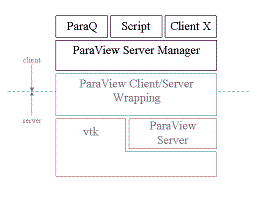
[[Image:script_architecture_diagram.gif]] | |||
ParaQ scripts will directly manipulate the SM through it's published API using one or more of the supported | ParaQ scripts will directly manipulate the SM through it's published API using one or more of the supported | ||
Revision as of 15:12, 3 October 2005
Requirements
ParaQ scripting requirements can be found here
Design
ParaQ scripting will be build on top of the server manager (SM) API. Main reasons behind this decision are:
- We need a scripting interface independent of the GUI (accessible through the python client)
- SM is designed to provide such an interface
- SM is already wrapped into Tcl, Python and client/server streams
ParaQ scripts will directly manipulate the SM through it's published API using one or more of the supported scripting languages (Python, Tcl and Java). A python client will be implemented (more on this later). In order to provide a easy-to-use, full featured and backwards compatible scripting language, the following guidelines will be followed:
- Clean separation of GUI/engine functionality. All the functionality to be accessed through the scripting interfaceshould be implemented in SM and accesses through the publish SM API by the GUI.
- Stable SM API. Since the scripting interface will depend on the SM interface, SM API should be stable and backwards compatible as much as possible. If possible, backwards compatibility should be automatically tested routinely.
- Clear and easy-to-use API. The SM API should be clear. Although the SM API is verbose due to it's design, simplifications can be made in the scripting language.
- Well documented. Wherever possible, documentation should be automatically generated from the code (a la doxygen and more). Where automatically generating the documentation is not possible, it should be hand generated.
Implementation details
Saving state/script
ParaQ will be able to save the SM state in two formats:
- XML
- Python scripts
Both will be generated from the in-memory representation of the state (stored as XML nodes) by either directly saving or parsing/converting. This will ensure that the code to save state is centralized and both are always in sync. Users will be able to edit and load both back into ParaQ (XML into both GUI and script clients, python into script client alone).
Script client
As mentioned above, there will be two ParaQ clients:
- Qt client
- Python client
Both will access the VTK layer through the server manager. Note that these are two separate applications. We do not plan to include a python interpreter in the Qt client. However, the python client should be able to connect to the server through sockets at the same time as the Qt client. This means both will be able to drive the same session simultaneously. In the short run, a python interpreter should be embedded in the Qt client to help debugging. This would be useful because the capability to connect multiple clients to one server (sync'ed server managers) will not be available initially. This interpreter should not be used from any C++ code. Also, it should in no way access the GUI (no Qt classes will be wrapped).
Note: When either client is running in standalone mode, the same process will be client and server at the same time. In theory, the other client should be able to connect to this process and issue SM command. Most probably, this will not be possible if the main process is the python client (i.e. python client is started first and is driving the server). Since python does not provide an event loop, it cannot listen to a socket and provide a user prompt.
Multiple sync'ed clients
Multiple (currently, two) clients will be able to connect to the same server. Here, server might be a separate process or part of a stand-alone client/server process. When a client connects to a server, it will populate it's SM state from the server and update it's GUI (no-op for python client). It will then be possible for both client to manipulate the SM. When SM state changes, it will invoke appropriate events to notify all clients. This will allow us to:
- load a python script to modify the state of both the python client and the Qt client
- load XML state in the same way (from either client)
- to programatically drive the visualization through the python client and have the GUI update itself in the process
Simplified SM API
The SM API is verbose. For example, to create a sphere proxy, modify the origin property and update the server, the following is required
proxy = proxyManager.NewProxy("sources", "SphereSource")
origProp = proxy.GetProperty("Origin")
origProp.SetElement(0, 0)
origProp.SetElement(1, 1)
origProp.SetElement(2, 0)
proxy.UpdateVTKObjects()
In python, we should be able to create appropriate proxy class to simplify this to:
proxy = proxyManager.NewPythonProxy("sources", "SphereSource")
proxy.SetOrigin(0,1,0)
proxy.UpdateVTKObjects()
We should also make sure that the help and function listing reflects this.